A recent paper in Frontiers in Genetics (a scientific publisher and research network) examined the genome of two dogs who lived to extremely old ages, 22 and 27 years old, and provides researchers with more information about what contributes to dogs becoming “centenarians.”
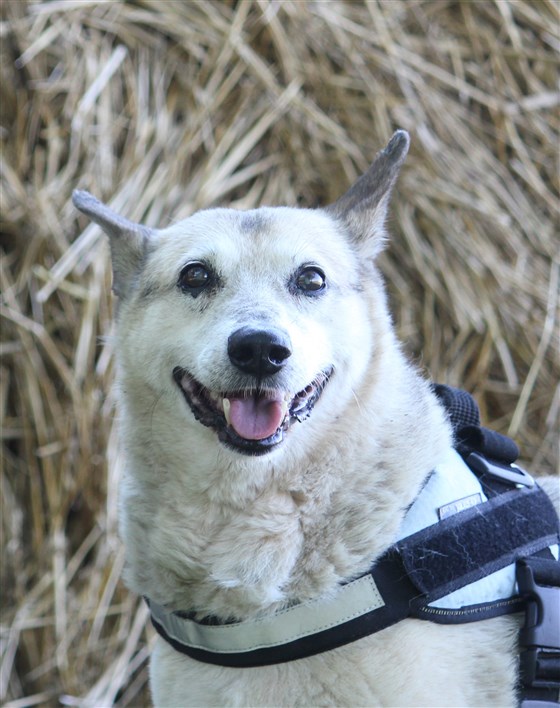


Start of the article: The hereditary discoveries may enable scientists to comprehend what makes a pooch solid into mature age and that impacts their people, too.Losing a canine is a terrible encounter for anybody regardless of the little guy’s age, and many wish their mutts could live longer lives. “On the off chance that we better comprehend the instruments of maturing in hounds, we can advance a more advantageous way of life for hounds,” Dávid Jónás, an examination individual at the Department of Ethology at Eötvös Loránd University in Budapest, Hungary, told TODAY through email. “In the event that pet pooches live more and more beneficial, it could have a positive effect on the mutts themselves, yet on the psychological wellness of their proprietors as well.”For this investigation, the scientists sequenced the DNA of two canines, Kedves, a 22-year-old female, and, Buksi, a 27-year-old male, what specialists called Methuselah hounds. These canines have a half longer life expectancy than others (much like a human centenarian). Specialists were searching for qualities they share that may clarify their all-encompassing life expectancy. “This was the principal study that researched the hereditary foundation of maturing in hounds utilizing entire genome sequencing techniques. We made the total DNA data of these pooches freely accessible for the two researchers and the overall population,” Jónás, the creator of the paper, said. “We distinguished qualities that are most likely connected to outrageous life span in hounds.” So what precisely did these qualities uncover?
All things considered, it’s somewhat muddled. “At the point when we inspected the around 20,000 canine qualities, we discovered a few purported start-and stop-codon transformations, which may bring about upset quality capacities. It is worth further inspecting these qualities: first to confirm that these changes are genuine positives, at that point to examine their natural impacts too,” noted Sára Sándor, a geneticist who was engaged with the exploration, in an official statement. A portion of the qualities that covered between their two genomes are identified with resistance, irritation and Alzheimer’s in humans.These discoveries helped them build up a speculation for additional examination with a bigger example size of old canines: “A pivotal hereditary necessity of outrageous life span exists in the tweaking (for example the predominant alignment) of quality expression.”While it is too early to state what this investigation implies for the normal pooch proprietor, having a superior comprehension of canine maturing may change how individuals may consider rearing mutts, said Carlos Alvarez, who was not engaged with the exploration.

“Something that (reproducers) might want the most is to make sound pooches,” said Alvarez, an important agent at the Research Institute at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio. “Breeding mutts to be solid is practically overpowering to consider. Nonetheless, in the event that you put the inquiry as far as life expectancy, the way that you have hereditary varieties that can increment or decline life expectancy, that is a lot simpler to think about.”Currently, individuals breed mutts to achieve a specific look —, for example, huge eyes or soft faces — and those looks frequently sway a puppy’s general wellbeing.

However, this new understanding about maturing may change how individuals consider hounds, Alvarez said. “We chose firmly for appearance attributes and by doing that we made mutts progressively defenseless for illnesses,” he said. “By doing hereditary investigations, we can begin to consider what we did and select now for wellbeing.”
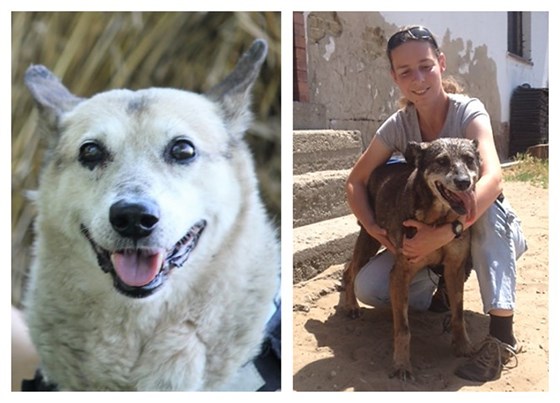

What’s more, the specialists presume that on the off chance that they comprehend what adds to solid maturing in hounds, they may pick up knowledge into how individuals age, as well.“It can also contribute to better understanding of the aging process in humans as well, because dogs share the same environment with their owners, which presumably makes the obtained results more relevant and applicable to human studies,” Jónás said. Another story in video: